What is Passwordless Authentication?
Passwordless authentication is a security method that allows users to access their accounts or systems without vulnerable traditional passwords. Instead, alternative methods such as biometrics and hardware tokens are used to prove identity. This approach enhances both overall security and user convenience.
Passwordless Authentication Definition
What does passwordless mean?
Passwordless authentication evolved as a response to the limitations and security challenges associated with traditional password-based systems. Users tend to choose weak and easily guessable passwords for the sake of being able to easily remember them, reuse them across multiple accounts, and fall victim to phishing attacks and credential theft.
However, the aforementioned are merely symptoms to the real vulnerability, which comes from reliance on a single knowledge factor. According to the 2023 Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report, over 66% of application attacks come from compromised passwords, and over 80% of data breaches involve compromised credentials.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA), which is both supplementary and a stepping stone towards passwordless authentication, was introduced to address some of these vulnerabilities introduced by reliance on passwords alone.
MFA combines the knowledge factor (such as a password) with a possession factor (such as a mobile device or token) and potentially an inherence factor (such as biometrics) for added security. Notably, while MFA enhances security, it may still involve some limited deployment of passwords.
The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) published the web authentication (WebAuthn) standard under the guidance of the FIDO Alliance, which enabled websites to use public key cryptography to conduct passwordless authentication using biometric logins, secure hardware tokens and other methods, such as via app notification on smartphones.
In fact, widespread adoption of smartphones with integrated biometric capabilities has undoubtedly contributed to the growth of secure, passwordless authentication. A number of factors have driven the adoption of strong authentication methods, including acceptance in verticals like tech, financial institutions, and healthcare providers, new mandates from both government regulations and industry standards, and user demand for a more convenient and secure experience. Passwordless authentication aligns with each of these and has created an opportunity to replace legacy forms of authentication.
Passwordless Authentication FAQs
What is Passwordless Authentication?
What is passwordless login? The goal of passwordless authentication is to use more secure and convenient authentication methods such as biometrics, hardware tokens or a supplementary mobile device for routine logins instead of traditional passwords. The passwordless strategy enhances security and improves the user experience by reducing friction and decreases the risk of attack.
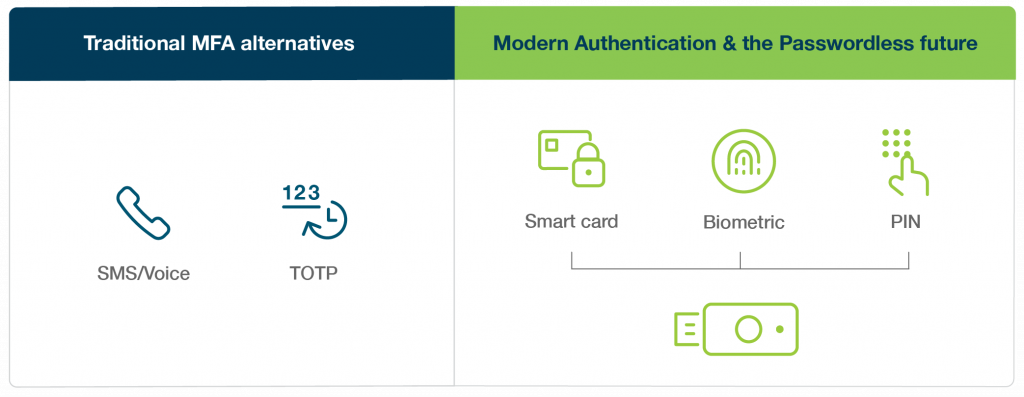
How Does Passwordless Authentication Work?
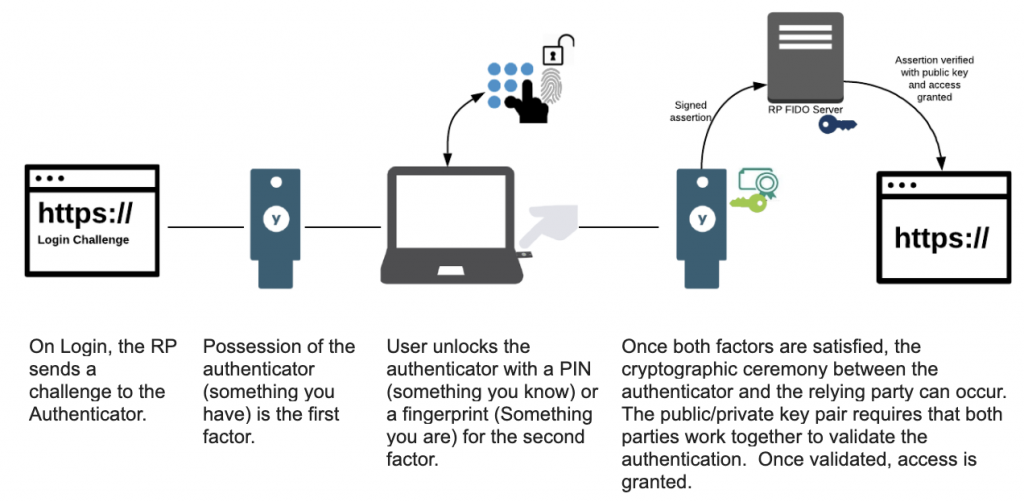
There are a range of alternatives that verify user identity without requiring a traditional password, although their specific mechanisms vary. However, a basic description of how passwordless authentication works generally includes a few common steps:
Registration and setup. During the initial account registration, the user typically provides a unique identifier, such as a username, an email address or phone number. This information becomes part of future user authentication requests. The user will also nominate and configure their primary authentication method, such as biometrics, hardware tokens, or another secure method (such as an app on their mobile device).
Authentication request. When the user attempts to login, the system will generate an authentication request. This authentication request results in the user receiving a request on screen to present their nominated authentication method, or through their registered email or mobile device, if these are applicable.
User response. Once the user receives the authentication request, they must approve it; the process for how the user responds depends upon the chosen authentication method.
Authentication verification. After the system receives the user’s response, whether it’s a biometric scan, hardware token approval or entering a one-time code, it verifies that the response matches with the user’s registered information or corresponds to the authentication request.
Access granted or denied. If the system is able to match the user’s response with the information configured during setup (including secret keys or seeds used to generate authentication requests), it grants access to the account. Otherwise, all other access requests are denied.
How Secure is Passwordless Authentication?
Is passwordless authentication safe? True passwordless security is actually a much more secure method of verifying a user’s identity, particularly compared to traditional password-based systems. However, its true strength largely depends on specific implementation and chosen authentication methods. Here are some factors that contribute to strong passwordless authentication:
Biometrics. Biometric passwordless authentication security such as fingerprint or facial recognition is generally considered very secure, although it may be prone to certain types of attacks, like spoofing using high-quality images or 3D models. The underlying logic typically relies on capturing a unique input that cannot be easily replicated by anyone beside the intended user.
Hardware tokens. Hardware tokens such as security keys that generate unique private cryptographic keys for each authentication request, offer a very high level of passwordless security and are typically resistant to phishing, keylogging attacks, SIM swapping, credential stuffing, adversary-in-the-middle attacks and brute force attacks.
Secure channel. Secure communication channels for authentication requests and responses are crucial. It is generally recommended to employ encryption and secure transmission protocols to protect data in transit over trusted channels, although there are even some methods to securely communicate over untrusted channels as well.
User experience. Improved user experience and added convenience are among the main benefits of passwordless authentication, and powerful factors driving users to adopt it. This in turn enhances secure access, because it reduces the likelihood of users resorting to insecure practices like password sharing or using weak passwords.
Account recovery. Although these are generally poorly defined strategies across vendors, systems and the wider community, reliable account recovery processes for when users lose access to their primary authentication methods remain important. If account recovery techniques offer a fallback to weaker mechanisms, attackers may be able to circumvent the stronger forms of authentication being implemented to protect the account in the first instance.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA). This is a process for authentication that combines more than one passwordless authentication factor, such as something the user has (e.g. a mobile device) and something the user is (e.g. biometrics) to enhance security.
Advantages of Passwordless Authentication
Passwordless authentication offers several advantages over traditional password-based systems:
Enhanced security. Passwordless authentication methods often rely on more secure authentication factors, such as biometrics or hardware tokens, reducing the risk of password-related vulnerabilities like weak passwords, password reuse and phishing attacks.
Reduced password fatigue. Users no longer need to remember complex passwords of a minimum length, containing a mix of upper and lower case letters and both alpha and non-alpha numeric characters, or reset them regularly. This reduces frustration and the use of insecure practices like writing down passwords as means to recall them.
Improved user experiences. Passwordless authentication UX delivers more convenience, increased productivity, higher user satisfaction, and a quicker login process.
Fewer account takeovers. With stronger authentication methods, the risk of unauthorized access to accounts is significantly reduced. This is especially important for sensitive or high-value accounts.
Simplifies IT operations. Decreased requests for password resets and assistance with forgotten passwords can lead to cost savings and improved operational efficiency.
Mitigation of credential stuffing attacks. Methods that eliminate passwords prevent attackers from using stolen or leaked passwords to gain unauthorized access to other services besides the original source of the stolen or leaked information, since users tend to reuse passwords across services.
Phishing resistance. Passwordless methods are often similarly resistant to phishing attacks because users are not prompted to enter their passwords. Even if a user’s authentication token or biometric data is compromised, it is typically useless without the physical corresponding device.
Passwordless MFA integration. Passwordless authentication is often combined with additional factors such (as a PIN or biometrics) to create an inherent multi-factor authentication system, adding an extra layer of security.
Compliance. Implementing passwordless authentication and stronger authentication measures can help organizations meet regulatory requirements and tighter security standards, such as those described under cyber insurance or federal mandates.
Scalability. It can be easier to scale passwordless authentication across various systems and platforms, especially in large organizations or for online services with numerous users.
Future-proofing. As technology evolves, passwordless methods can adapt to new and more secure authentication mechanisms, ensuring that security remains up-to-date.
Device compatibility. Many modern devices, such as smartphones and laptops, come equipped with biometric sensors (fingerprint or facial recognition), making it easier for users to adopt passwordless authentication.
Types of Passwordless Authentication
Some common types of passwordless authentication solutions include:
Biometrics/inherence factors. Biometric passwordless technology relies on a sample of unique physical or behavioral traits of the user, such as fingerprint reading, facial recognition, iris scanning, voice recognition or palm vein patterns. Users access their accounts after their biometric sample is successfully verified against the stored reference data.
One-time passwords (OTPs). OTPs are temporary, often time-sensitive codes, sent to the user via email, SMS or a mobile app. While not truly “passwordless”, OTP usage does reduce reliance on static, reusable passwords by supplementing with another authentication factor.
Push notifications. Users receive a push notification on a registered mobile device as they attempt to log in that they can approve or deny, often used to supplement an authentication process, but may also be used to circumvent the need to enter a password entirely.
Mobile device passwordless authentication methods. Users authenticate themselves using their smartphones, which can in itself include various methods such as device biometrics (e.g. Touch ID or fingerprint), device possession (e.g. proximity to a paired device), or a secure mobile app with its own authentication parameters or processes.
Smart cards and tokens. Smart cards and hardware tokens incorporate cryptographic keys for authentication. Users typically insert the card or connect the token to their device to complete the authentication process, using the stored secret key to sign or encrypt a random challenge that can be verified by the requesting party.
Email magic links. Users receive a uniquely generated link in their email. Clicking the link logs them in directly without the need for a password.
Social media passwordless login services. Many of the large technology companies such as Google, Facebook, Apple and Microsoft, are also Identity Service Providers (IdPs) which allow other services access to their authentication and a subset of user account information. After users have successfully authenticated themselves to one or more of the aforementioned IdPs, secure session information is then sent to the nominated external service about the identity of the user, so there is often no need for additional verification.
Examples of Passwordless Authentication
Here are some examples of passwordless authentication companies and solutions:
Passkeys / FIDO passwordless / WebAuthn passwordless. The Fast Identity Online (FIDO2) and WebAuthn standards originally enabled passwordless authentication by using public key cryptography, typically via purpose-built and device-bound hardware, whilst passkeys also add the ability to sync across devices using a cloud service. Users register a cryptographic public private key pair, and for each login, the stored private key is used to sign a challenge presented by the relying party, and verified using the public key.
Microsoft Hello. Microsoft passwordless authentication capabilities come in the form of Windows Hello, a solution that allows users to log in to Windows devices using facial recognition, fingerprint or PIN. Hello Azure passwordless authentication is integrated into Windows 10 and Windows 11, and there is even Windows Hello for Business that can be used for enterprise authentication.
Apple Face ID and Touch ID. Apple iOS devices and Macs use facial and fingerprint recognition for secure and convenient login and to authorize transactions.
Google Smart Lock. One of the passwordless authentication Google capabilities for Android devices comes from Google Smart Lock. This feature allows users to keep their Android devices unlocked when using from trusted locations, or in the presence of other trusted, connected devices.
Auth0 passwordless. This platform offers passwordless authentication auth0 capabilities through email links, magic links and one-time codes.
Okta. Okta’s Identity Cloud offers passwordless authentication through mobile app authentication and WebAuthn. It’s commonly used for enterprise identity management.
Passwordless authentication AWS. Options for passwordless authentication in the Amazon Web Services (AWS) ecosystem include AWS Cognito and AWS Single-Sign-On (AWS-SSO).
Duo Security (Cisco). Duo offers MFA solutions including mobile app authentication and WebAuthn.
Yubico. The Yubikey hardware security key supports FIDO2/WebAuthn and PIV among many other protocols, offering strong passwordless authentication for a wide range of platforms and services.

Ping Identity. Ping Identity offers a variety of identity and access management solutions, including passwordless authentication using mobile app authentication and FIDO2.
Authenticator apps. Authenticator apps like Google Authenticator and Microsoft Authenticator offer passwordless authentication for personal and enterprise accounts by generating one-time codes or using push notifications for approval.
Social login. Platforms like Facebook, Google, and Apple allow users to login to many other websites and apps using existing profiles.
Biometric authentication on mobile devices. Many mobile devices come with built-in biometric authentication methods like fingerprint reading and facial recognition, which can be used for passwordless access to the device and associated services.
How to Implement Passwordless Authentication
Implementing passwordless authentication typically involves a series of steps:
Define organizational objectives. Clearly delineate organizational goals and objectives for passwordless authentication in terms of security, user experience and operational efficiency.
Choose the authentication method. Select one or more passwordless authentication methods that align with user objectives and their needs, in addition to the security risk profile of accessible information as determined by the enterprise. Generally speaking, the more sensitive the information, the stronger the authentication method should be.
Integration and development. Implement the nominated authentication method(s) using any software development kits, libraries, or APIs provided by selected vendors, or potentially, a comprehensive solution offered by one or more vendors.
User registration. Allow users to register their authentication method during the account creation process if necessary. This may involve capturing biometric data, registering a hardware token or setting up a mobile app. WebAuthn users will need to enroll their devices and generate cryptographic keys for example, so it is critical that clear instructions and user guidance are provided during this process.
User recovery and backup. Implement a secure process for account recovery and provide a backup authentication method if possible. It is important to note that an insecure backup method may be used to circumvent the entire system, so its importance should not be underestimated.
Monitoring and maintenance. Continuously monitor passwordless authentication system performance and ensure that security patches are updated, and any security concerns are promptly addressed.
User education. Educate users about how to go passwordless and provide clear instructions on how to set up, use and recover from the selected authentication method.
Compliance and documentation. Ensure the implementation complies with relevant regulatory requirements. Maintain documentation of authentication procedures for auditing and accountability.
User feedback and iteration. Gather feedback from users to identify any usability or security concerns and make necessary incremental improvements to the system. Follow best practices and keep security and user privacy at the forefront throughout the implementation process.
Does Yubico Support Passwordless Authentication?
Yes, Yubico supports passwordless authentication through their hardware security keys and the use of the WebAuthn standard.
YubiKeys are compatible with a wide range of platforms and services that support WebAuthn and passkeys, making it a versatile option for passwordless authentication.
Learn more about how Yubico’s passwordless authentication solutions can help your enterprise transition into a passwordless future here.
Learn more about Yubico’s Passwordless Authentication here.
Get started

Find the right YubiKey
Take the quick Product Finder Quiz to find the right key for you or your business.

